1. MySQL多表查询
我们之前都是对一张表数据查询,进行条件约束,限制,过滤等等
本节主题
- 多表连接查询
- 复合条件连接查询
- 子查询
准备数据表
这里两张表,并没有绑定外键约束关系
#创建部门表
create table department(
id int,
name varchar(20)
);
#创建员工表
create table employee(
id int primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(20),
sex enum('male','female') not null default 'male',
age int,
dep_id int
);
#插入数据
insert into department values
(200,'技术'),
(201,'人力资源'),
(202,'销售'),
(203,'运营');
insert into employee(name,sex,age,dep_id) values
('egon','male',18,200),
('alex','female',48,201),
('wupeiqi','male',38,201),
('yuanhao','female',28,202),
('liwenzhou','male',18,200),
('jingliyang','female',18,204)
;
#检查数据和结构
mysql> desc department;
mysql> desc employee;
mysql> select * from department;
mysql> select * from employee;
1.1.1. 多表连接查询
select 字段 from 表1 inner|left|right join 表2 on 表1.字段 = 表2.字段;
笛卡尔积
select * from employee,department;
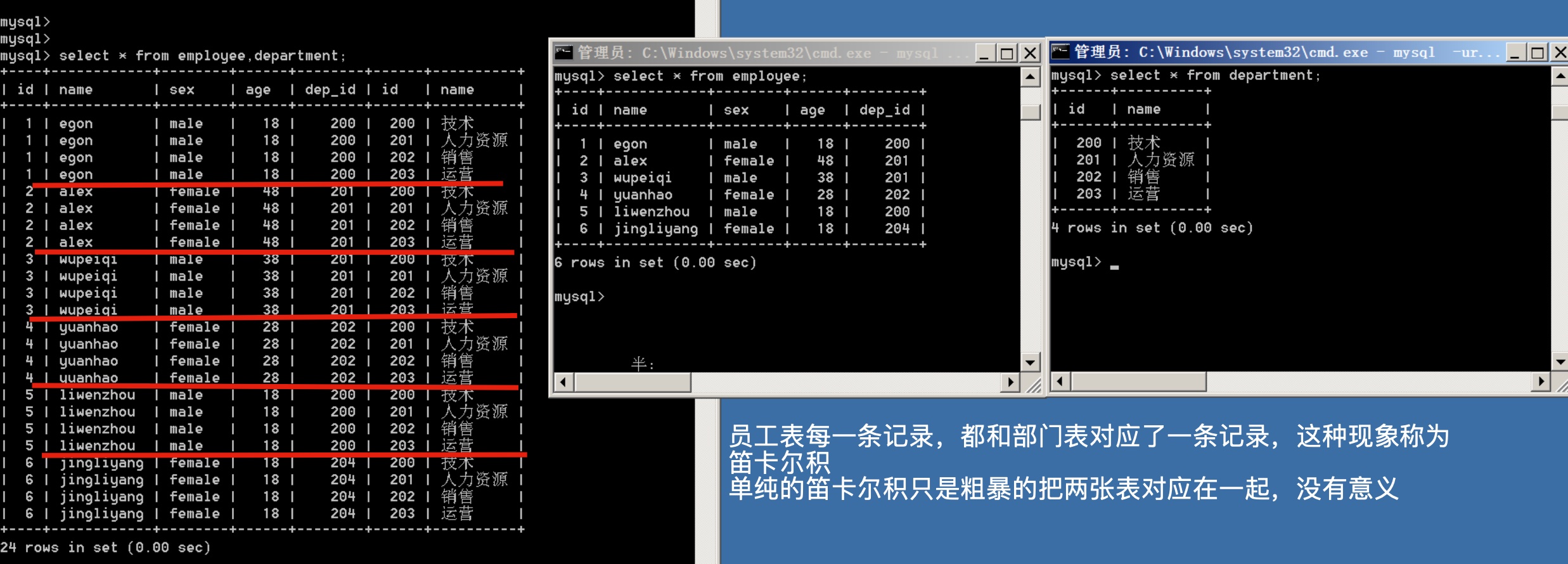
左表每一条记录都和右表对应了一条记录,称为笛卡尔积,单纯的笛卡尔积没有意义,简单粗暴的把两张表对应在一起。
1.1.2. 在笛卡尔积上,添加对应关系
我们想要的是,部门和员工,正确一一对应的数据
mysql> select * from employee,department where employee.dep_id = department.id;
+----+-----------+--------+------+--------+------+----------+
| id | name | sex | age | dep_id | id | name |
+----+-----------+--------+------+--------+------+----------+
| 1 | egon | male | 18 | 200 | 200 | 技术 |
| 2 | alex | female | 48 | 201 | 201 | 人力资源 |
| 3 | wupeiqi | male | 38 | 201 | 201 | 人力资源 |
| 4 | yuanhao | female | 28 | 202 | 202 | 销售 |
| 5 | liwenzhou | male | 18 | 200 | 200 | 技术 |
+----+-----------+--------+------+--------+------+----------+
5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
数据是出来, 但是不用这种low的方式,mysql提供了关键字,更方便查询
1.1.3. 内连接,只连接匹配的行
只取出两张表的共同部分,相当于从笛卡尔积中找出正确的结果
#这种方式,后面还可以继续where条件判断,优于上述SQL
select * from employee inner join department on employee.dep_id = department.id;
#如果想自定义字段显示,可以别用*,改如下SQL
select employee.id,employee.name,employee.age,employee.sex,department.name from employee inner join department on employee.dep_id=department.id;
+----+-----------+------+--------+----------+
| id | name | age | sex | name |
+----+-----------+------+--------+----------+
| 1 | egon | 18 | male | 技术 |
| 2 | alex | 48 | female | 人力资源 |
| 3 | wupeiqi | 38 | male | 人力资源 |
| 4 | yuanhao | 28 | female | 销售 |
| 5 | liwenzhou | 18 | male | 技术 |
+----+-----------+------+--------+----------+
5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
1.1.4. 左连接
在内连接的基础上,保留左边表的数据
#以左表为准,即找出所有员工信息,当然包括没有部门的员工
#本质就是:在内连接的基础上增加左边有右边没有的结果
mysql> select * from employee left join department on employee.dep_id=department.id;
+----+------------+--------+------+--------+------+----------+
| id | name | sex | age | dep_id | id | name |
+----+------------+--------+------+--------+------+----------+
| 1 | egon | male | 18 | 200 | 200 | 技术 |
| 5 | liwenzhou | male | 18 | 200 | 200 | 技术 |
| 2 | alex | female | 48 | 201 | 201 | 人力资源 |
| 3 | wupeiqi | male | 38 | 201 | 201 | 人力资源 |
| 4 | yuanhao | female | 28 | 202 | 202 | 销售 |
| 6 | jingliyang | female | 18 | 204 | NULL | NULL |
+----+------------+--------+------+--------+------+----------+
6 rows in set (0.00 sec)
#优化显示结果
mysql> select employee.id,employee.name,department.name as depart_name from employee left join department on employee.dep_id=department.id;
+----+------------+--------------+
| id | name | depart_name |
+----+------------+--------------+
| 1 | egon | 技术 |
| 5 | liwenzhou | 技术 |
| 2 | alex | 人力资源 |
| 3 | wupeiqi | 人力资源 |
| 4 | yuanhao | 销售 |
| 6 | jingliyang | NULL |
+----+------------+--------------+
1.1.5. 右连接
在内连接的基础上,找出右边表的数据
#以右表为准,即找出所有部门信息,包括没有员工的部门
#本质就是:在内连接的基础上增加右边有左边没有的结果
mysql> select * from employee right join department on employee.dep_id=department.id;
+------+-----------+--------+------+--------+------+----------+
| id | name | sex | age | dep_id | id | name |
+------+-----------+--------+------+--------+------+----------+
| 1 | egon | male | 18 | 200 | 200 | 技术 |
| 2 | alex | female | 48 | 201 | 201 | 人力资源 |
| 3 | wupeiqi | male | 38 | 201 | 201 | 人力资源 |
| 4 | yuanhao | female | 28 | 202 | 202 | 销售 |
| 5 | liwenzhou | male | 18 | 200 | 200 | 技术 |
| NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 203 | 运营 |
+------+-----------+--------+------+--------+------+----------+
6 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select employee.id,employee.name,department.name as depart_name from employee right join department on employee.dep_id=department.id;
+------+-----------+--------------+
| id | name | depart_name |
+------+-----------+--------------+
| 1 | egon | 技术 |
| 2 | alex | 人力资源 |
| 3 | wupeiqi | 人力资源 |
| 4 | yuanhao | 销售 |
| 5 | liwenzhou | 技术 |
| NULL | NULL | 运营 |
+------+-----------+--------------+
1.1.6. 子查询
子查询就是把一个SQL放在一个括号里,当做另一个SQL的条件。
#1:子查询是将一个查询语句嵌套在另一个查询语句中。
#2:内层查询语句的查询结果,可以为外层查询语句提供查询条件。
#3:子查询中可以包含:IN、NOT IN、ANY、ALL、EXISTS 和 NOT EXISTS等关键字
#4:还可以包含比较运算符:= 、 !=、> 、<等
查询平均年龄在25岁以上的部门名
#分析,这句话可以理解为,先求出部门平均年纪在25岁以上的,然后再知道部门名字
select id,name from department
where id in
(select dep_id from employee group by dep_id having avg(age) > 25);
查询技术部员工名字
#找出员工信息,是否存在技术部门表中
select name from employee
where dep_id in
(select id from department where name='技术');
查询人数少于2个的部门
#分析,对员工信息进行分组,统计组内人数小于2的
#再进行子查询,查询部门名字
mysql> select name from department where id in (select dep_id from employee group by dep_id having count(dep_id)<2);
+------+
| name |
+------+
| 销售 |
+------+
1 row in set (0.01 sec)